High-Level Design
The Fiscal Information Exchange (iFIX) platform employs a hexagonal architecture, also known as the Ports and Adapters pattern, to facilitate seamless and standardized fiscal data exchange among various government entities. This architectural approach ensures that the core business logic remains isolated from external systems and technologies, enhancing flexibility and maintainability.
Key Components of iFIX Architecture
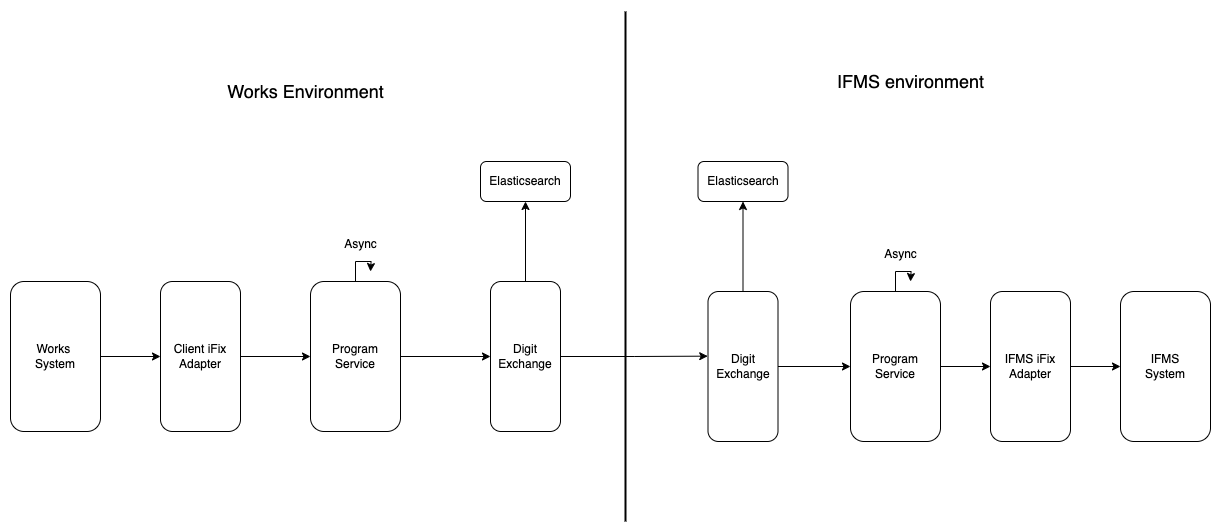
DIGIT Exchange
DIGIT Exchange acts as the secure and trusted bridge between independently deployed systems that need to communicate fiscal data. It ensures data integrity, non-repudiation, and secure transmission between producers (like program services) and consumers (like IFMS or auditing tools).
Core Responsibilities:
Message Authentication & Signing: Ensures that all outgoing and incoming messages are cryptographically signed and verified, preventing tampering and ensuring authenticity.
Event Publishing: Each successfully exchanged message is logged as an event. These events are published to Kafka and pushed to Elasticsearch to support operational dashboards and real-time monitoring.
Interoperability Backbone: DIGIT Exchange makes it possible for different organizations or departments to operate independent systems while still collaborating and sharing data securely.
Audit Trail & Observability: Tracks and stores the flow of all messages to enable full traceability and debugging capabilities across the exchange network.
Program Service
The Program Service is the domain-specific core service within iFIX that manages fiscal operations — including sanctions, allocations, and disbursements — under defined financial programs.
Key Features & Responsibilities:
Program Definition: Allows administrators to define “programs” — logical boundaries for budget and fund flow such as health campaigns, infrastructure projects, or welfare schemes.
Transaction Management: Each fiscal transaction (e.g., allocation or disbursement) is linked to a program and governed by its lifecycle.
Validation & Business Rules: All incoming messages from the adapter are validated against business rules. This ensures that transactions are complete, legitimate, and follow the proper hierarchy of approval.
Interaction with DIGIT Exchange: Valid messages are forwarded to DIGIT Exchange for further routing to external financial systems (e.g., IFMS). Invalid messages are rejected with precise error codes.
State Management: Maintains records of program-wise amounts sanctioned, allocated, committed, and available for disbursement — enabling accurate fiscal control and audit readiness.
Adapters
Adapters are the integration glue of the iFIX ecosystem. They decouple the internal working of iFIX from the unique data formats, protocols, and workflows of external systems.
There are two types of adapters:
Producer Adapter: Sits on the side of a department or donor system that generates fiscal data.
Consumer Adapter: Placed at the system which is the recipient of fiscal data (e.g., an IFMS or treasury system).
Core Functions & Advantages:
Data Transformation & Mapping: Converts messages between iFIX’s standardized fiscal event format and the target system’s native format (e.g., XML, JSON, SOAP). This ensures seamless compatibility regardless of the external system’s design.
System-Agnostic Integration: Adapters can be easily configured or extended to integrate iFIX with any kind of system, including legacy platforms, ERP solutions, MIS dashboards, or financial gateways.
Validation & Enrichment: Adapters can enrich messages (e.g., attaching metadata) or perform pre-validation before sending data to core services or external endpoints.
Reusability & Portability: Once an adapter is built for a particular system (like a state’s IFMS), it can be reused across other programs or departments, accelerating rollouts.
Loose Coupling: Adapters ensure that changes in external systems do not impact the core iFIX services, enabling independent evolution and easier upgrades.
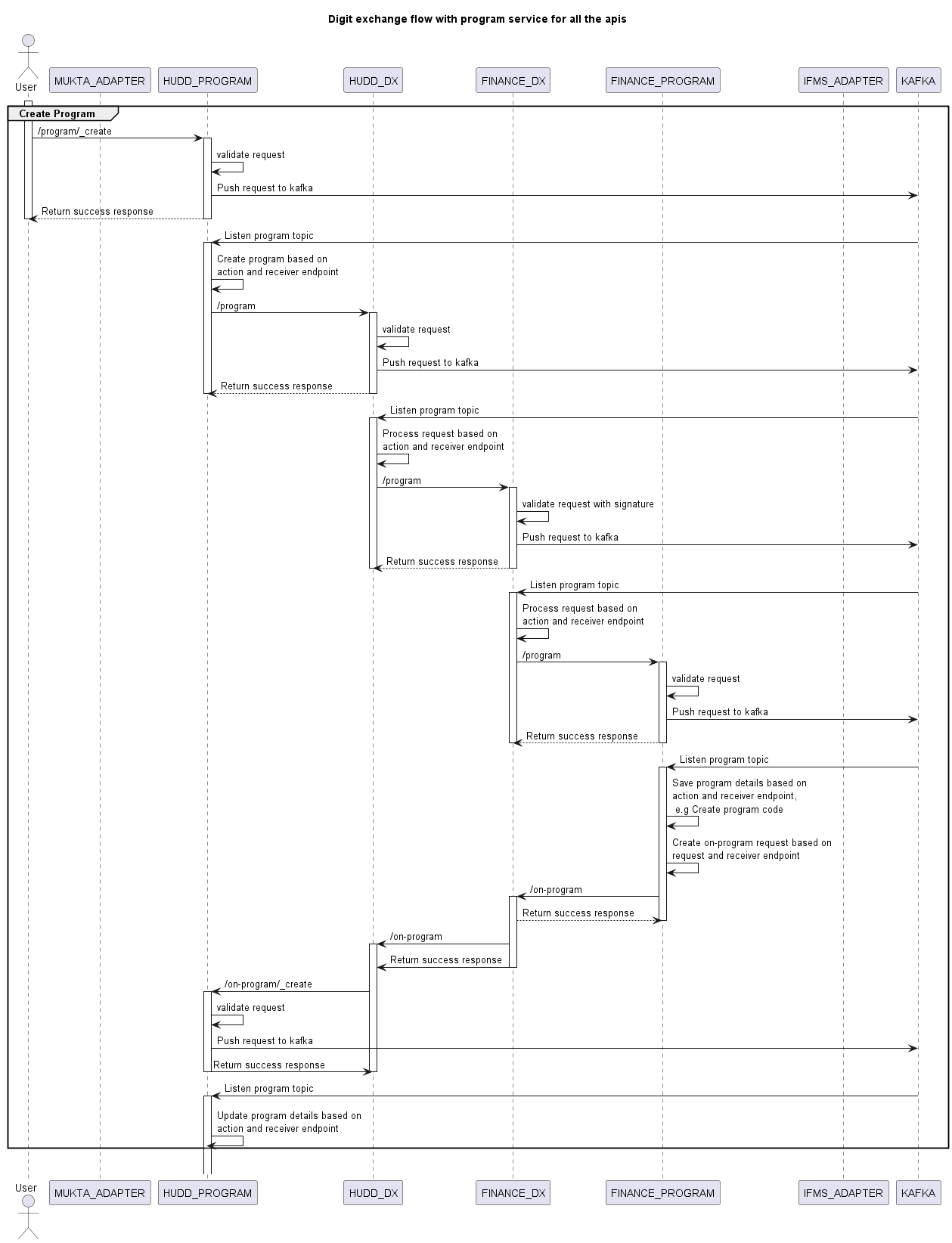
Sequence Diagram
Last updated
Was this helpful?